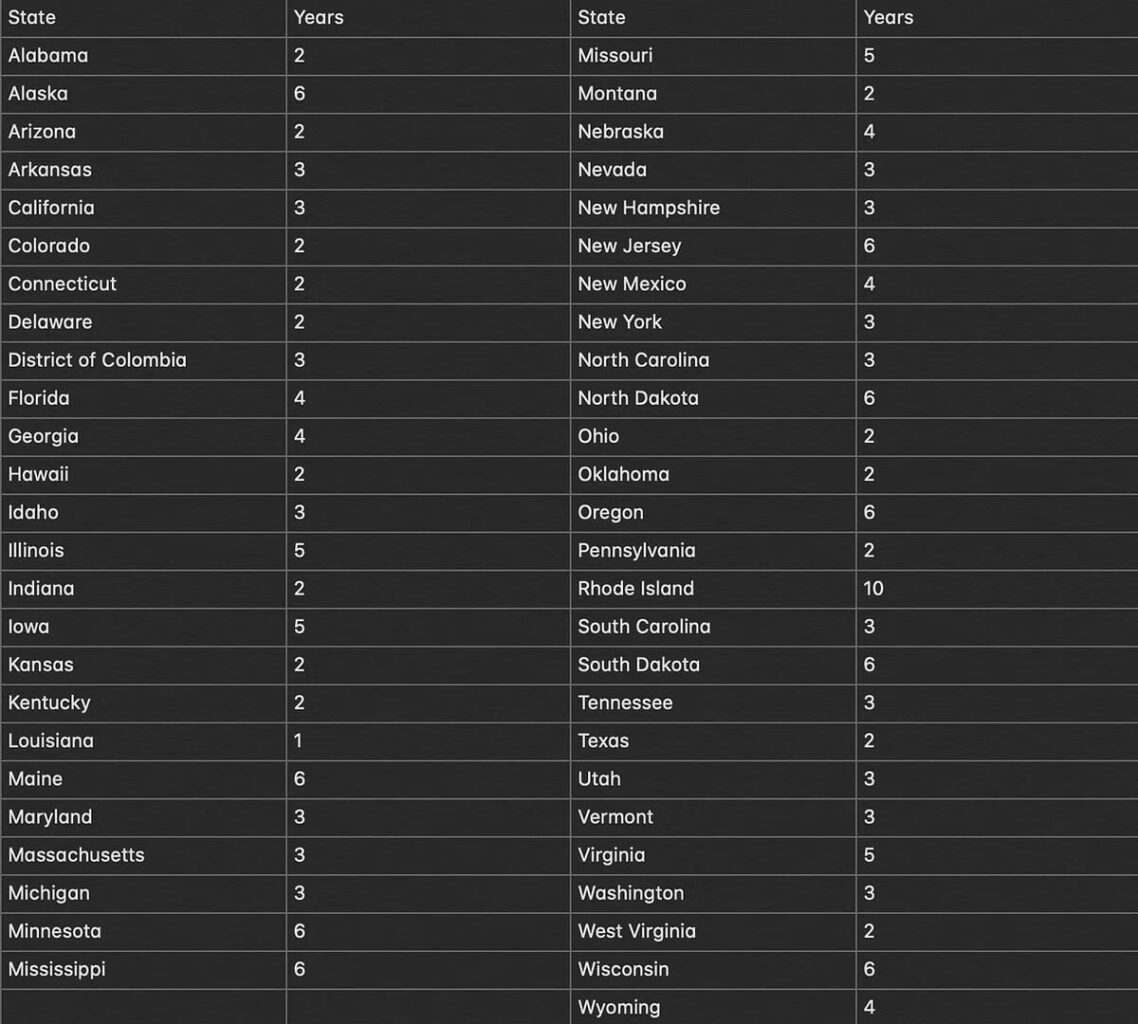
Diminished value of your vehicle is recoverable in third-party cases only. You can only recover from third-party at fault insurance companies and you cannot make a claim under your own uninsured motorist insurance. All drivers must carry minimum liability insurance, and the statute of limitations is 4 years from the time of the accident. Title 1-1-135.
Reposa v. Buhler, 770 P.2d 235, 238 (Wyo. 1989).
Damages must be proven with a reasonable degree of certainty. Id. While exact certainty is not required, remote, conjectural or speculative damages will generally be insufficient.
In Meredith GMC, Inc. v. Garner, 78 Wyo. 396, 328 P.2d 371 (Wyo. 1958) the Wyoming Supreme Court cited with approval Restatement of Torts § 928 (1939). It provides:
Where a person is entitled to a judgment for harm to chattels not amounting to a total destruction in value, the damages include compensation for
(a) the difference between the value of the chattel before the harm and the value after the harm or, at the plaintiff’s election, the reasonable cost of repair or restoration where feasible, with due allowance for any difference between the original value and the value after repairs, and (b) the loss of use.
The Wyoming Supreme Court has explained that there are two options for calculating damages, either the “cost-of-repairs method” or the “decrease- market value method.” Aetna Casualty & Sur. Co. v. Langdon, 624 P.2d 240, 242 (Wyo. 1981). The appropriate method varies depending on the circumstances, and there is no absolute rule defining when each method should be applied. Bush v. State, 2003 WY 155, ¶ 25, 79 P.3d 1178, 1187 (Wyo. 2003) (Lehman J. dissenting). As the language of § 928(a) suggests, a plaintiff in Wyoming might be able to seek from a tortfeasor the reasonable costs of repairing a damaged vehicle plus the difference between the original value and the value after repairs.